How to Recognize Skin Cancer Early – The Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Skin cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer worldwide, but the good news is that it's also one of the most treatable—especially when detected early. Recognizing the signs of early stage skin cancer can significantly improve the chances of successful melanoma treatment. Whether you’ve noticed unusual spots, changes in moles, or new growths on your skin, knowing what to look for could make all the difference.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Understanding Skin Cancer and Melanoma: What’s the Difference?
Skin cancer primarily appears in three forms: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. While basal and squamous cell carcinomas are more common and typically less aggressive, melanoma is the most dangerous form. Melanoma develops in melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment, and can spread rapidly if not detected early.
What Are the Early Warning Signs of Skin Cancer?
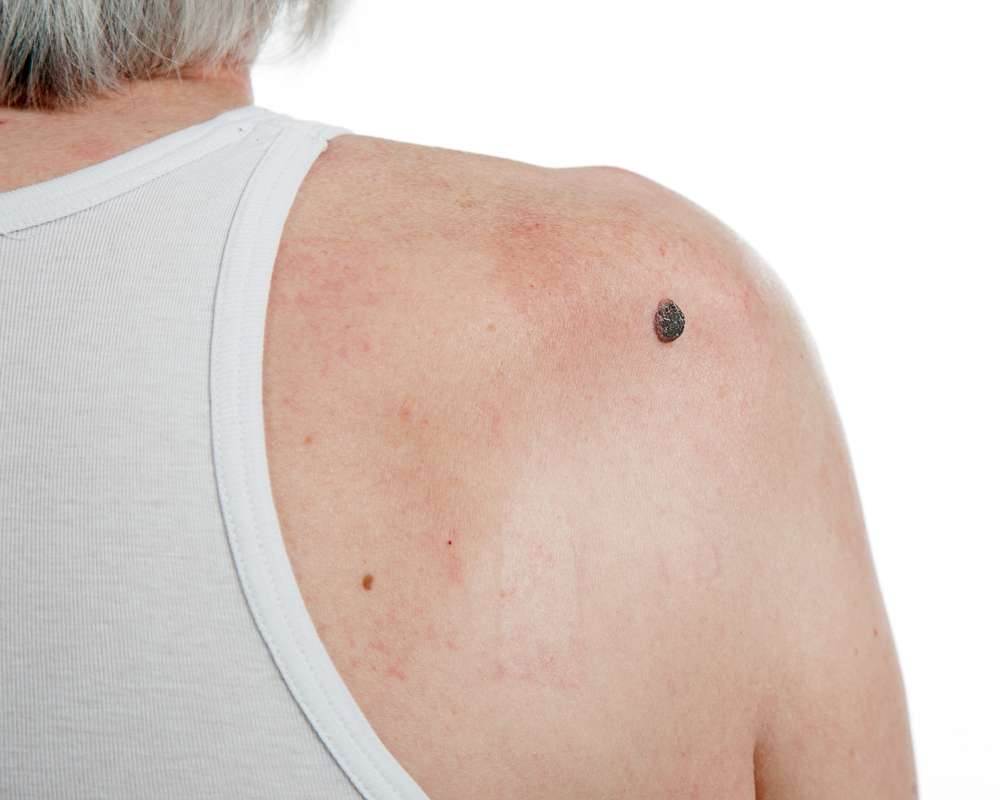
The ABCDE rule is a valuable tool for identifying potential melanomas:
-
Asymmetry: One half doesn’t match the other
-
Border: Irregular, ragged, or poorly defined edges
-
Color: Varying shades of brown, tan, or black; sometimes red, blue, or white
-
Diameter: Larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser)
-
Evolving: Changes in size, shape, color, or elevation
How Should You Perform Regular Skin Checks?
Conduct monthly self-examinations in a well-lit room with a full-length mirror. Examine your entire body, including hard-to-see areas like your back, scalp, and between toes. Use a hand mirror for difficult-to-view areas and document any unusual spots with photos for comparison over time.
When Should You See a Healthcare Provider?
Schedule an appointment with a dermatologist if you notice:
-
New moles or skin changes appearing after age 30
-
Spots that are different from others (“ugly duckling” signs)
-
Moles that itch, bleed, or don’t heal
-
Any significant changes in existing skin marks
-
Family history of skin cancer with new skin concerns
What Are the Risk Factors for Skin Cancer?
Several factors can increase your risk of developing skin cancer:
-
Fair skin, light hair, or light eyes
-
History of sunburns, especially in childhood
-
Frequent sun exposure or tanning bed use
-
Family history of skin cancer
-
Multiple moles or atypical moles
-
Weakened immune system
-
Living in high-altitude or sunny climates
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis typically begins with a visual examination by a dermatologist, followed by a biopsy if concerns are identified. Treatment options vary based on the type, stage, and location of the cancer:
| Treatment Type | Best For | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Excision | Small, defined tumors | 2-4 weeks |
| Mohs Surgery | Face, sensitive areas | 1-2 weeks |
| Radiation Therapy | Inoperable cases | Several weeks |
| Immunotherapy | Advanced melanoma | Ongoing |
| Chemotherapy | Widespread melanoma | Several months |
Treatment costs and recovery times may vary significantly based on individual cases, insurance coverage, and location. Please consult healthcare providers for specific information about your situation.
Remember, prevention is crucial in skin cancer management. Use broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, wear protective clothing, avoid peak sun hours, and never use tanning beds. Regular skin checks and prompt medical attention for concerning changes are your best defense against skin cancer.




